
Once the reboot has completed you will be able to use the root account with your newly set password.Īs shown we can reset the root password in Linux CentOS/RHEL 7 by booting with the ‘rd.break’ option, remounting the file system with read/write privileges, creating a chroot jail, executing the passwd command and then finally fixing up SELinux contexts.Īfter exiting the chroot and the initramfs root shell prompt the file system will be relabelled which may take a few minutes or more depending on the number of files you have. Enter the ‘exit’ command twice, the first one will exit the chroot jail environment while the second will exit the initramfs root shell and reboot the system.For a plain vanilla CentOS 7 server, it takes me about 2 minutes to complete. Note that this may take some time depending on the amount of files you have on the file system. Create the /.autorelabel command using ‘touch’.Ĭreating this file will automatically perform a relabel of all files on next boot. As SELinux is not running in this mode the file is created with no SELinux contexts, which can cause problems when we reboot. This is because when the ‘passwd’ command is run, it creates a new /etc/shadow file.


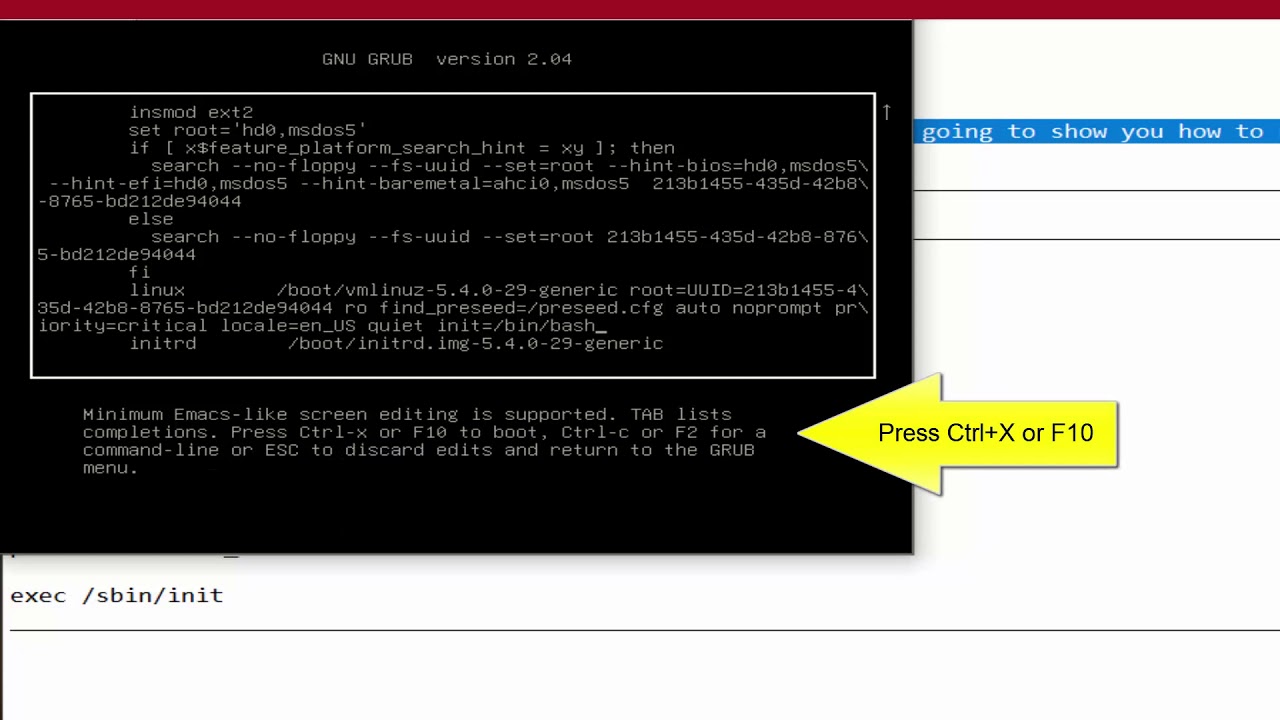
Enter ‘rd.break’ without quotes at the end of this line, as shown below.
#Reset root password centos 6.10 how to
This is also a task that you will need to know how to perform for the RHCSA exam. From version 7 the equivalent modes are the rescue or emergency targets, however these require the root password before you can do anything which doesn’t help us here, so we’ll take you through the new process to change the lost root password. The process has changed from CentOS/RHEL (Red Hat Enterprise Linux) version 6 to 7, as previously you would boot into single user mode and then change the password as root. Normally resetting the root password is a simple task if you’re logged in already with root privileges, however if you forget the password and need to change it things become a little more difficult.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
